Had Period Then Started Bleeding Again Vaginal Dryness
Vaginal haemorrhage betwixt periods
Bleeding betwixt periods; Intermenstrual bleeding; Spotting; Metrorrhagia
This commodity discusses vaginal bleeding that occurs betwixt a woman's monthly menstrual periods. Such bleeding may be called "intermenstrual bleeding."
Related topics include:
- Dysfunctional uterine haemorrhage
- Heavy, prolonged, or irregular menstrual periods
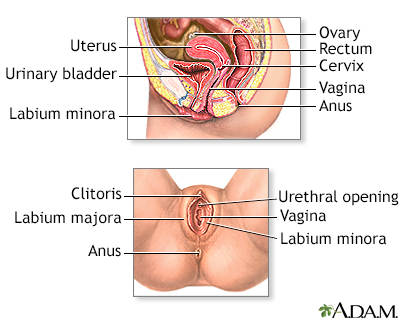
External structures of the female reproductive anatomy include the labium minora and majora, the vagina and the clitoris. Internal structures include the uterus, ovaries, and cervix.
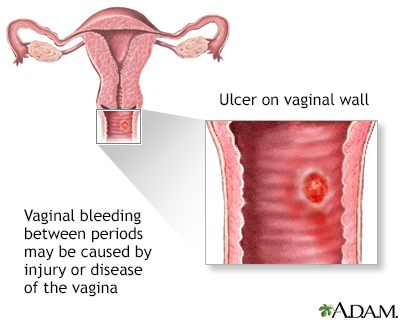
Normal menstrual flow lasts about 5 days and produces a full claret loss of sixty to 250 mL and occurs every 28 days. There are several causes of abnormal vaginal bleeding and a careful exam past a health intendance provider is oft the best way to sort out the source of the haemorrhage.
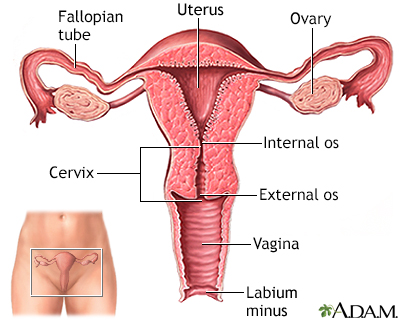
The uterus is a hollow muscular organ located in the female pelvis between the bladder and rectum. The ovaries produce the eggs that travel through the fallopian tubes. One time the egg has left the ovary information technology tin can be fertilized and implant itself in the lining of the uterus. The main function of the uterus is to nourish the developing fetus prior to birth.
Considerations
Normal menstrual flow lasts nearly 5 days. It produces a total claret loss of 30 to 80 mL (most 2 to viii tablespoons), and occurs commonly every 21 to 35 days.
Vaginal bleeding that occurs between periods or later menopause can exist caused by various problems. Nearly are benign and tin can be hands treated. Sometimes, vaginal bleeding may be due to cancer or pre-cancer. Therefore, any unusual haemorrhage should exist evaluated right abroad. The gamble for cancer increases to nearly ten% in women with postmenopausal haemorrhage.
Make sure that bleeding is coming from the vagina and is not from the rectum or the urine. Inserting a tampon into the vagina will confirm the vagina, neck, or uterus equally the source of bleeding.
A careful exam by your health care provider is most frequently the best way to find the source of the haemorrhage. This test can be done even while you are bleeding.
Causes
Causes may include:
- Uterine fibroids or cervical or uterine polyps
- Changes in hormone levels
- Inflammation or infection of the neck (cervicitis) or uterus (endometritis)
- Injury or disease of the vaginal opening (caused by intercourse, trauma, infection, polyp, genital warts, ulcer, or varicose veins)
- IUD utilise (may crusade occasional spotting)
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Miscarriage
- Other pregnancy complications
- Vaginal dryness due to lack of estrogen afterwards menopause
- Stress
- Using hormonal birth control irregularly (such every bit stopping and starting or skipping nativity control pills, patches, or estrogen rings)
- Underactive thyroid (low thyroid function)
- Apply of blood thinners (anticoagulants)
- Cancer or pre-cancer of the cervix, uterus, or (very rarely) fallopian tube
- Pelvic exam, cervical biopsy, endometrial biopsy, or other procedures
Home Care
Contact a provider correct away if haemorrhage is very heavy.
Keep track of the number of pads or tampons used over fourth dimension and so that the amount of bleeding can exist determined. Uterine blood loss can be estimated by keeping rails of how oft a pad or tampon is soaked and how often one needs to be inverse.
If possible, aspirin should be avoided, equally it may prolong bleeding. Withal, NSAIDS such equally ibuprofen can be used to minimize haemorrhage and cramping.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Telephone call your provider if:
- You are meaning.
- At that place is any unexplained haemorrhage betwixt periods.
- There is any haemorrhage later menopause.
- At that place is heavy bleeding with periods.
- Aberrant haemorrhage is accompanied past other symptoms, such as pelvic pain, fatigue, dizziness.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
The provider will perform a concrete test and ask questions almost your medical history. The concrete exam volition include a pelvic exam.
Questions near the bleeding may include:
- When does the bleeding occur and how long does it terminal?
- How heavy is the bleeding?
- Practise you have cramps also?
- Are there things that brand the bleeding worse?
- Is in that location annihilation that prevents information technology or relieves it?
- Exercise you lot have any other symptoms such as abdominal pain, bruising, pain when urinating, or claret in urine or stools?
Tests that may be done include:
- Claret tests to check thyroid and ovarian function
- Cervical cultures to check for a sexually transmitted infection
- Colposcopy and cervical biopsy
- Endometrial (uterine) biopsy
- Pap smear
- Pelvic ultrasound
- Saline infusion sonohysterogram
- Hysterosonogram
- Hysteroscopy
- Pregnancy test
Most causes of intermenstrual bleeding are easily treatable. The trouble can most oftentimes exist diagnosed without besides much discomfort. Therefore, it is important not to delay in having this trouble evaluated by your provider.
References
Bulun SE. Physiology and pathology of the female reproductive axis. In: Melmed Southward, Auchus RJ, Goldfine AB, Koenig RJ, Rosen CJ, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 17.
Ellenson LH, Pirog EC. The female genital tract. In: Kumar V, Abbas AK, Aster JC, eds. Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Illness. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 22.
Ryntz T, Lobo RA. Abnormal uterine haemorrhage: etiology and management of astute and chronic excessive bleeding. In: Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. seventh ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2017:chap 26.
Singh Five, Mishra B, Sinha S, Agrawal South, Thakur P. Role of saline infusion sonohysterography in infertility evaluation. J Hum Reprod Sci. 2018;11(three):236-241. PMID: 30568352
Version Info
Last reviewed on: 4/14/2021
Reviewed by: John D. Jacobson, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Colina Linda, CA. Besides reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Managing director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Managing director, and the A.D.A.Grand. Editorial team.

mcnicollknewhervel.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/symptoms/vaginal-bleeding-between-periods
0 Response to "Had Period Then Started Bleeding Again Vaginal Dryness"
Post a Comment